Negative emotion is an incredibly volatile fuel. Our CEO, Dane Jensen, lays out how to harness its energy for building motivation in his latest article for Harvard Business Review titled Turn Your Team’s Frustration into Motivation.
In the article, Dane offers three tools for leaders to motivate people facing a setback:
🏷 Label the negative emotion and engage. Right or wrong, giving it a name helps uncover important information that can be used for moving forward.
👏 Feed the self-coach, not the self-critic. Encourage them to look for the opportunity in the crisis.
🛴 Channel energy to action. Use the moment to build a vision of a better future and build clarity around what it takes to get there.
Strong leaders don’t shy away from negative emotions. They lean into them and help their people use them to recover and grow.
Click here to read the article on hbr.org.
In 2002, the Canadian Women’s National Hockey Team entered the Olympic Games in Salt Lake City in an unfamiliar position: as underdogs. They had not hit their stride as a team, their confidence had taken a hit, and emotions were at risk of boiling over. In eight head-to-head games against the Americans leading up to the Olympics, Canada had lost all eight. For many players, it was hard to avoid memories from four years earlier when the team had lost to the Americans in the gold medal game.
Jayna Hefford, who was playing in the first Games of her Hall of Fame career, recalls the point when the stress and emotion came to a head: “There was an intense conversation in the dressing room with the team. A lot of people had a lot to say about things we needed to do and how we were going to get better, and we realized that a lot of what was happening was the blame game.”
“We realized that a lot of what was happening was the blame game.”
Through a frank, players-only discussion the team was able to come together, but the conversation could have gone a number of different ways. It stayed on track because the team was prepared – mentally and emotionally – to have performance conversations under pressure and surface a number of issues the team needed to resolve. And that preparation turned out to be an important stepping stone to winning gold in Salt Lake City.
Training the bomb squad
Handled poorly, team communication under pressure can lead to combustion. And just like you wouldn’t get success as a bomb disposal technician going in without their toolkit, you won’t find success in communicating through tense situations if your team isn’t prepared. The advantage the women’s team had that allowed them to emerge from that conversation united was a deep awareness of their communication tendencies and systems to counteract the counterproductive ones. They had laid the foundation for performance conversations in good times so that they could happen and be productive when the difficulty hit.
In other words: they had a tool kit and they knew how to use it.
“The biggest opportunity for meaningful growth is often to increase self-awareness and strengthen their ability to communicate productively when under pressure.”
We’ve worked with hundreds of teams in elite sport and business, including the last four medal-winning Canadian women’s hockey teams. One of the things we’ve learned is that when teams are already operating at a high level, the biggest opportunity for meaningful growth is often to increase their self-awareness and strengthen their ability to communicate productively when under pressure. To support this, we’ve developed a process to help teams become more aware of their tendencies, develop systems and practice performance conversations anytime.
At the heart of this process is a tool called the TAIS – The Attentional and Interpersonal Styles inventory. The TAIS was developed for use by Navy SEALs and Olympic athletes, and we’ve found it to be an incredibly valuable tool for diagnosing communication challenges on all kinds of teams. When the pressure is on, when teams are in the midst of setbacks and failure, individuals will fall back on their default communication styles.
Five communication choices
The author of the TAIS, Dr. Robert Nidefer, showed that people make five choices over and over in the course of a conversation. These choices are informed by their tendencies on five dimensions.
Give up/take control – are you more likely to try to take control, or cede control to someone else?
Speed up/slow down – are you more likely to force action or a decision, or encourage more thought and consideration?
Extroverted/introverted – are you going to seek out others, or try to solve the problem yourself?
Become quiet/express thoughts – are you going to become quiet and try to understand, or advocate for your position?
Critique/express support – will you say no and become more critical, or will you say yes and express support?
Cut the right wire
Every team will have members with different tendencies. Ultimately, it’s not the tendencies that matter; it’s the level of awareness team members have of their tendencies, and the systems they put in place to leverage their strengths and weaknesses in the heat of the moment. The highest performing teams we work with take three critical steps in preparing for productive communication under any circumstances.
Acknowledge the “I” in team
Great coaches know that the phrase “there is no I in team” is a myth. Every individual makes their own contribution – and without self-awareness, people can’t adjust. That’s why the first step in your team’s communication action plan is to encourage every individual to build self-awareness across these five choices. By knowing and understanding their default tendencies, team members can begin to recognize their behaviour and course-correct when necessary for the good of the team.
Connect to the “we” of the team
It’s advantageous to know your individual tendencies, and the value is multiplied when that information is shared with everyone on the team. When you raise the waterline of team awareness, everyone can work on the same communication system. Team members can see the intent behind the behaviors their teammates exhibit. The process can be incredibly difficult; Team Canada Captain Hayley Wickenheiser called sharing her profile with her team-mates, “the most stressful part of the 4-year [Olympic] quadrennial.”
Come together as a team
Armed with knowledge of self and others, teams can come together and translate self-awareness into action. When pressure hits, if everybody on the team has the tendency to get louder, express their thoughts and try to take control of the conversation, the team can make decisions in advance to decide who’s going to take control when issues arise. By having these conversations earlier, teams can build systems to fall back on when the pressure is turned up.
Preventing detonation
The next time you’re headed into a potentially high stakes conversations, use the five choices below to carry out a short 3-step preparation exercise:
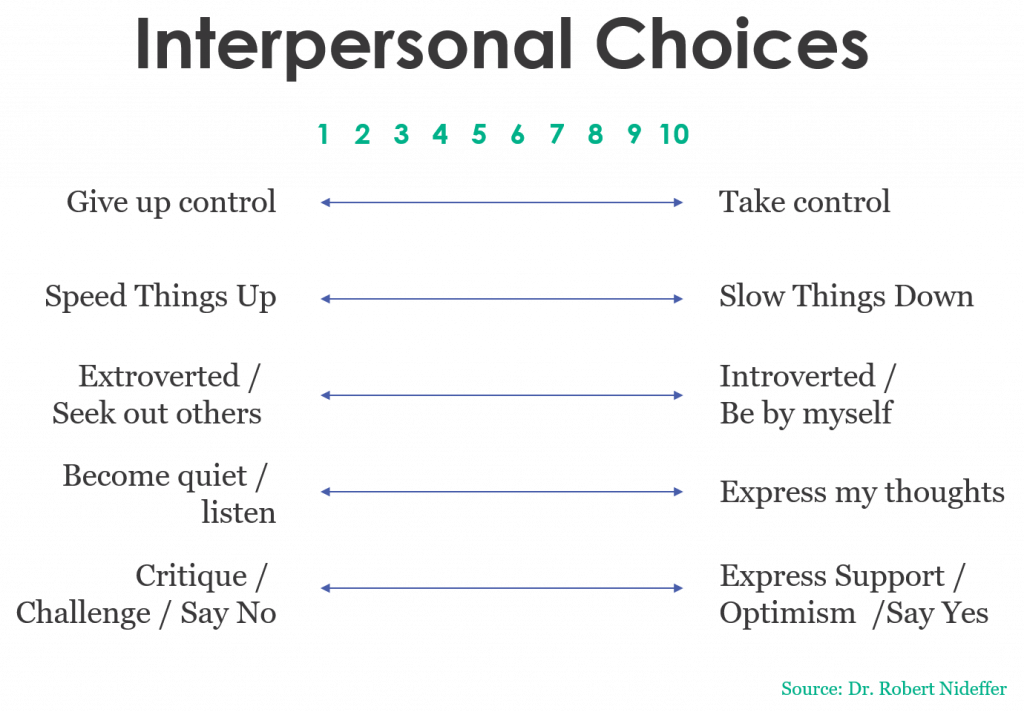
1. Plot your default tendency on each of the five scales – given your past history, where are you most likely to fall?
2. Where would you ideally like to be as you head into this specific interaction?
3. What are the gaps between your ideal and default style? What actions will you take to ensure you are at your ideal?
Repurpose the fuel for growth
We’ve said before that negative emotion is volatile fuel. Improperly handled, it can lead to combustion. Used properly, it can lead to high performance.
Team communication must go beyond just staying cool during difficult times. Teams must use communication to understand and lean in to their negative emotions, uncover what the emotions are telling them, and frame it as an opportunity for growth. This is what happened with the women’s team in 2002. They prepared to have productive communication at all times, and used the tools they learned to find the opportunity for growth at a moment when it could have blown up. Jayna Hefford explains:
By understanding your individual communication style, sharing your tendencies with the team and proactively planning to address potential faults, your team can find its way through difficult times and not just safely diffuse difficult situations but find new strength and opportunity for higher performance in the process. By Dane Jensen / CEO, Third Factor
All teams suffer setbacks. What separates resilient teams from the rest is how they respond. Resilient teams come back stronger after failure because leaders and team members lean into the negative emotions that inevitably accompany setbacks and use the energy under those emotions to fuel recovery.
Negative emotion is volatile fuel
Heading into the women’s World Cup in 2011, Canada’s national soccer team was one of the favourites. Two weeks later, they were knocked out of the round robin in a 4-0 defeat to France and headed home without winning a game – finishing dead last.
“It wasn’t going to define us”
Team Captain Christine Sinclair talked about feeling “humiliated” – like they had let down the country. And yet just one year later, the same team outperformed at the London Olympics to win Canada’s first ever medal in soccer. “We knew what we were capable of and just because we had one bad tournament it wasn’t going to define us,” said Sinclair. The head coach of the Women’s National Team, John Herdman, spoke about how the team was “an easy group to motivate” because they had just suffered such a crushing defeat.
Negative emotion can be powerful fuel for positive response. It can provide ‘bulletin board material’ that leads to determination, and ultimately harder work and higher standards.
But negative emotion is highly volatile fuel. If not handled correctly, it can trigger a negative feedback loop that leads to the blame game and teams that end up either combusting or just detaching.
Three Jobs for Leaders of Resilient Teams
We’ve observed that leaders of resilient teams are able to trigger the positive feedback loop from negative feedback by doing three things differently than leaders of less resilient teams:
1. Lean into negative emotion
Leaders of resilient teams don’t retreat from negative emotion. They don’t try to rescue people from it and make them feel good. Rather, they use it for its developmental potential.
The psychologist Roberto Assagioli has said, “a psychological truth is that trying to eliminate pain merely strengthens its hold. It is better to uncover its meaning, include it as an essential part of our purpose and embrace its potential to serve us.”
When leaders try to reassure people or make the pain go away, they rob it of its power. It is better to acknowledge the pain and embrace it so that it can be used to fuel growth.
“As painful as it feels now, it will help him.”
So, what does ‘leaning in’ look like? Consider “the shot.” Kawhi Leonard’s quadruple bouncing Game 7 buzzer beater was a moment of euphoria for Toronto. On the other side, however, it was a devastating moment for a young Philadelphia 76ers team featuring 25-year-old star Joel Embiid, who left the court in tears. When asked about the emotional response of Embiid in the post-game press conference, Philadelphia head coach Brett Brown said, “As painful as it feels now, it will help him. It will help shape his career.” Rather than shying away from the pain, comforting Embiid and trying to lessen the sting, Brown leaned into it and helped his young player see it as a growth opportunity – a sign that he needed to work harder.
2. Frame negative emotion differently
Leaders of resilient teams have a different answer to the question “what is this pain telling us?” than leaders of less resilient teams.
They frame pain as a signal that they aren’t there yet – rather than a sign that they aren’t good enough. As a result of this framing, resilient teams respond to negative emotion with determination. They get committed to the challenges they face by exerting control where it matters: their own effort.
After a lacklustre season heading into Salt Lake City in 2002, the Canadian women’s hockey team held a player’s only meeting where they came up with the acronym WAR, for ‘We Are Responsible.’ As 4-time gold medalist Janya Hefford reports, “there was a lot of the blame game going on”– and the WAR framing helped them redirect attention away from the officiating, their opponents, etc. and towards what they were responsible for. Ultimately, this perspective proved vital in overcoming 8 straight penalties in the Gold-Medal game to triumph.
3. Channel negative emotion
After embracing negative emotion and finding its meaning, teams and their leaders must still channel the emotion into positive outcomes. Our founder, Peter Jensen, will often ask teams who have suffered failure one powerful question: “What are we going to do with the energy under this emotion?”
it’s easy to channel emotion into what Ben Zander has called “the conversation of no possibilities” and allow the dangerous side of negative emotion affect to take over. Channeling negative emotion productively requires individuals on teams to take responsibility for redirecting energy towards growth and hard work.
Negative emotion is fuel for growth
Resilient teams process negative emotion in a way that leads to harder work and higher standards as opposed to detachment or combustion. They do that by leaning into negative emotion rather than retreating, by framing it a little differently and by seeing it with a sense of challenge, control and commitment.
As a leader, your job is to create the conditions that allow negative emotion to be used to its full potential. The next time your team suffers a setback, encourage your team to accept their feelings, find meaning in their failure, and channel their emotions to come back stronger than before. On November 19th, 2019, 75 leaders from Toronto’s business and HR communities gathered at OCAD U CO for a discussion on team resilience. Here’s what they learned:
Leading the discussion, Third Factor CEO Dane Jensen brought together the voices of elite athletes and coaches to talk about what separates those teams that are able to rebound from failure to reach even higher levels of performance from teams that tend to crumble or falter in the face of failure.
Drawing on insights from our work with high-performing sports teams, including the last four medal winning women’s Olympic hockey teams and the men’s and women’s national soccer teams, Dane identified what it takes for teams to not just perform but also to recover and be resilient. These are the four traits we’ve observed that characterize resilient teams, or differentiate resilient teams from those that are less resilient:
1. Negative emotion. Resilient teams process negative emotion in a way that leads to harder work and higher standards as opposed to detachment or combustion. They frame it so rather than being scared of negative emotion, they choose to lean into it, work with it, and see it with a sense of challenge, control and commitment.
2. Communication. The teams that recover quickly from setbacks communicate differently because they have worked consciously on awareness. They’ve surfaced their communication styles and worked on having performance conversations in the good times.
3. Relationships. Teams are more resilient when they work diligently on building relationships, even if that’s just 30 seconds for each person every day.
4. Shared purpose. Teams work best in the face of failure when they have a clear a line of sight to shared purpose. They don’t do hard work for it’s own sake, but because they choose to connect it to something that actually matters to them.
JOIN US FOR OUR NEXT LEARNING BREAKFAST
Be the first to know about upcoming learning opportunities from Third Factor by entering your information below.
Determining what you can and can’t control is the key to harnessing the tremendous instructive power of adversity.
Even when we lack control over certain circumstances, we will still have control over how we will deal with these circumstances, what perspective we will choose to take. In this whitepaper, Sandra Stark and Peter Jensen explore three aspects that comprise a resilient perspective during a time where many businesses began to lose hope – the global economic crisis.
Though the Great Recession is now behind us, the inner skills that they address will help you flourish in the face of adversity and grow in even the poorest of conditions.
Click here to download the whitepaper. Valuing lessons from failure is an important mindset in business, but in reality most teams aren’t prepared to fail. The consequences of failure can breed negativity and erode team culture, destroying productivity, preventing future success, and masking the very lessons that make failure valuable in the first place.
In our 25 years of experience working with hundreds of teams in the worlds of elite sport, business, not-for-profit, Government and Academia – including the last 4 medal-winning Canadian Women’s Olympic hockey teams – we’ve observed the characteristics that define resilient teams, and the steps they and their leaders take to use failure as a catalyst for growth and high performance.
In this keynote address, Third Factor CEO, Dane Jensen, will draw on the lessons we’ve learned from the Olympic athletes we’ve worked with to inspire you with new ideas to foster resilience on teams in your organization by examining four characteristics of resilient teams.
SORRY WE MISSED YOU
This event has passed, but it won’t be the last. Be the first to know about future events from Third Factor by entering your information below.
The presentation features the voices of athletes and coaches who have persevered in the face of failure and tremendous pressure, including:
- Hayley Wickenheiser, 4-time Olympic Gold Medallist, women’s hockey
- Jayna Hefford, 4-time Olympic Gold Medallist, women’s hockey
- Christine Sinclair, 2-time Olympic Medallist and captain of the Canadian Women’s National Soccer Team
- Roy Rana, Assistant Coach, Sacramento Kings
- Dr. Peter Jensen, Founder, Third Factor
Participants will learn:
- How resilient teams harness and channel the negative emotions associated with loss and disappointment
- How their communication systems allow them to work through setbacks more productively and therefore recover faster
- How the relationships amongst team members can support or hinder recovery, and
- The vital role that a strong shared purpose plays in making it through the hard times
You should attend if:
- You are responsible for enabling and fostering team culture in your organization
- You are responsible for fostering a culture of innovation in your organization
- You want new ideas on how to maintain productivity and performance through difficult times
- You want to build resilience for yourself or your team
Set against the backdrop of one of Toronto’s newest and most exciting innovation spaces, OCAD U CO, participants will enjoy great peer networking and a delicious breakfast.
About the presenter:
 Dane Jensen
Dane Jensen is a cross-pollinator between the podium and the boardroom. As CEO of Third Factor, he works every day to enhance Canada’s business and athletic competitiveness through better strategy and stronger leadership. His clients include RBC, CIBC, WestJet, University Health Network, the Canadian Paralympic Committee, the Canadian Sport Institute Ontario, and Right To Play. He has worked as an advisor to Senior Executives in 12 countries on 5 continents, he contributes regularly to The Globe and Mail on the topics of strategy and leadership, and was previously an Associate Partner at the strategy consultancy Monitor Deloitte.
About the venue:

Just minutes from Union Station on Toronto’s waterfront,
OCAD U CO is a state-of-the-art 14,000 square foot studio designed specifically for collaborative innovation work. The space features is home to 20 resident design-led startups, a suite of formal and informal meeting spaces, and is the setting for our program,
How To Lead Innovation, which we run in partnership with OCAD U CO and the Smith School of Business at Queen’s University.
Reserve your spot:
SORRY WE MISSED YOU
This event has passed, but it won’t be the last. Be the first to know about future events from Third Factor by entering your information below.
What do elite athletes know about resilience? They know that it is largely an inside job.
In the face of adversity, disappointment, and set-backs, Olympic athletes take on the role of Power Converters: they harness the energy inherent in pressure to enhance their own performance. Here’s the good news: you too can learn to leverage pressure in order to generate better results. The necessary skills are not innate genetic gifts, but rather, abilities that can be consciously learned and practiced.
Peter and Dane Jensen introduce the four skill sets that make up the personal resilience tool-kit used by elite athletes and high performers in business to gain control over how pressure and stress will impact performance.
Click here to download the whitepaper. Upon hearing the ‘c-word’ from his doctor, Peter Jensen embraced teachings from the Inside Edge in order to equip him for the challenge ahead.
Imagine if you got a phone call that would dramatically change your life for the next decade or more. How would you react? The mental fitness skills that are used to stimulate high performance on the field or in the boardroom have a distinct purpose in a more central area of our lives–our personal health.
Click here to read the whitepaper.


 Dane Jensen is a cross-pollinator between the podium and the boardroom. As CEO of Third Factor, he works every day to enhance Canada’s business and athletic competitiveness through better strategy and stronger leadership. His clients include RBC, CIBC, WestJet, University Health Network, the Canadian Paralympic Committee, the Canadian Sport Institute Ontario, and Right To Play. He has worked as an advisor to Senior Executives in 12 countries on 5 continents, he contributes regularly to The Globe and Mail on the topics of strategy and leadership, and was previously an Associate Partner at the strategy consultancy Monitor Deloitte.
Dane Jensen is a cross-pollinator between the podium and the boardroom. As CEO of Third Factor, he works every day to enhance Canada’s business and athletic competitiveness through better strategy and stronger leadership. His clients include RBC, CIBC, WestJet, University Health Network, the Canadian Paralympic Committee, the Canadian Sport Institute Ontario, and Right To Play. He has worked as an advisor to Senior Executives in 12 countries on 5 continents, he contributes regularly to The Globe and Mail on the topics of strategy and leadership, and was previously an Associate Partner at the strategy consultancy Monitor Deloitte.
 Just minutes from Union Station on Toronto’s waterfront, OCAD U CO is a state-of-the-art 14,000 square foot studio designed specifically for collaborative innovation work. The space features is home to 20 resident design-led startups, a suite of formal and informal meeting spaces, and is the setting for our program, How To Lead Innovation, which we run in partnership with OCAD U CO and the Smith School of Business at Queen’s University.
Just minutes from Union Station on Toronto’s waterfront, OCAD U CO is a state-of-the-art 14,000 square foot studio designed specifically for collaborative innovation work. The space features is home to 20 resident design-led startups, a suite of formal and informal meeting spaces, and is the setting for our program, How To Lead Innovation, which we run in partnership with OCAD U CO and the Smith School of Business at Queen’s University.